Managing multi-day retreats demands seamless coordination, yet over 60 percent of American event planners report that fragmented communication often leads to costly scheduling setbacks. The pressure intensifies when international teams, tight deadlines, and diverse expectations collide in large organizations. Adopting shared event planning models empowers corporate managers to engage expertise from across departments, reduce individual burdens, and navigate the complexities of global event coordination with greater flexibility and efficiency.
Table of Contents
- Defining Shared Event Planning Models
- Core Processes And How Participation Works
- Types Of Shared Event Planning Solutions
- Key Challenges And Coordination Risks
- Comparing Shared Tools And Traditional Methods
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Collaborative Approach | Shared event planning emphasizes distributed responsibilities, enhancing teamwork and leveraging diverse expertise. |
| Communication Tools | Implement centralized digital dashboards for real-time visibility and effective coordination among team members. |
| Flexibility and Adaptation | Emphasize flexible roles and adaptive decision-making processes to effectively manage event complexities. |
| Coordination Challenges | Be proactive in addressing risks through clear role definitions and robust communication strategies. |
Defining Shared Event Planning Models
Shared event planning represents a collaborative approach to organizing complex gatherings that requires synchronized efforts across multiple stakeholders. Unlike traditional event management where a single coordinator handles all details, shared planning models emphasize distributed responsibilities and cross-functional teamwork. This methodology enables organizations to leverage diverse expertise and resources while minimizing individual workload.
The core philosophy of shared event planning revolves around creating flexible, integrated frameworks where different departments or team members contribute specialized skills toward a common objective. Typical models include matrix-based structures where roles are clearly defined, accountability is distributed, and communication channels remain transparent. Event planners might establish cross-functional committees with representatives from finance, marketing, logistics, and human resources to ensure comprehensive coverage of all event dimensions.
Key characteristics of effective shared event planning models include transparent role definitions, robust communication protocols, and adaptive decision-making processes. Organizations typically establish a primary coordinator who facilitates interactions, tracks progress, and ensures alignment with overarching event goals. These models require sophisticated coordination tools that allow real-time collaboration, task assignment, and status tracking across potentially geographically dispersed teams.
Pro tip: Implement a centralized digital dashboard that provides real-time visibility into each team member's tasks, dependencies, and progress to streamline shared event planning efforts.
Core Processes and How Participation Works
Shared event planning centers on structured collaboration that transforms traditional event management into a dynamic, interactive process. Collaborative participation strategies involve creating comprehensive frameworks where multiple stakeholders contribute specialized knowledge and skills toward achieving common event objectives. These approaches fundamentally differ from hierarchical models by distributing responsibilities and empowering team members to engage actively throughout the planning lifecycle.
The core processes typically involve establishing clear communication channels, defining explicit roles, and implementing accountability mechanisms. Organizations often develop detailed responsibility matrices that outline specific tasks, decision-making authority, and expected contributions from each team member or department. Key stakeholders might include representatives from finance, marketing, logistics, human resources, and other relevant functional areas who collaboratively shape event strategy, design, and execution.

Successful participation requires robust coordination tools and transparent workflows that enable real-time information sharing and seamless collaboration. This might involve digital platforms that allow simultaneous task management, progress tracking, and interdepartmental communication. Effective shared event planning models also emphasize flexibility, allowing team members to adapt roles and responsibilities as event complexities evolve while maintaining a unified vision and clear performance expectations.
Pro tip: Develop a centralized digital dashboard that provides real-time visibility into individual team member contributions, task dependencies, and overall project progress to enhance collaborative event planning efficiency.
Types of Shared Event Planning Solutions
Shared event planning solutions have evolved dramatically, offering increasingly sophisticated digital platforms that transform collaborative event management. Conference management systems provide comprehensive tools that enable seamless coordination across multiple organizational domains, integrating complex workflows into unified digital environments. These solutions range from comprehensive enterprise platforms to specialized collaborative tools designed for specific event types and industry requirements.
The primary categories of shared event planning solutions include integrated management platforms, virtual event systems, and collaborative scheduling tools. Enterprise-level solutions typically offer end-to-end features such as abstract submission, peer review processes, registration management, program scheduling, and financial transaction capabilities. More specialized platforms focus on specific aspects like interactive participant engagement, real-time communication channels, and dynamic session management that support complex collaborative scenarios.
Modern shared event planning solutions emphasize flexibility, interoperability, and user-friendly interfaces that accommodate diverse organizational needs. These platforms often incorporate advanced features like artificial intelligence-driven recommendations, predictive analytics for attendee engagement, and customizable workflow configurations. Key technological capabilities might include multi-stream event support, private invitation mechanisms, interactive presentation formats, and comprehensive community-building tools that enable seamless global collaboration.
Pro tip: Select a shared event planning solution that offers robust integration capabilities and provides granular permission controls to ensure data security while maintaining collaborative flexibility.
Key Challenges and Coordination Risks
Shared event planning introduces complex coordination challenges that can significantly impact organizational effectiveness and event success. Group coordination dynamics reveal multiple potential risks including misaligned stakeholder expectations, communication breakdowns, and uneven participation levels. These challenges emerge from the intricate interactions between diverse team members, each bringing unique perspectives, priorities, and working styles to the collaborative process.
The primary coordination risks in shared event planning encompass logistical complexity, financial constraints, and technical infrastructure limitations. Organizations must navigate potential pitfalls such as scheduling conflicts, resource allocation disputes, and divergent decision-making approaches. Critical risk areas include managing competing stakeholder demands, maintaining transparent communication channels, adapting to unexpected changes, and ensuring consistent engagement across distributed team members.
Mitigating these coordination risks requires implementing robust strategic approaches that emphasize clear role definition, proactive communication protocols, and adaptive management techniques. Successful strategies involve establishing explicit expectations, developing comprehensive conflict resolution mechanisms, and leveraging collaborative technologies that facilitate real-time information sharing. Advanced shared event planning models incorporate sophisticated tools that provide visibility into individual contributions, track interdependencies, and enable rapid adjustments to emerging challenges.
Summary of major coordination risks in shared event planning and strategies to address them:
| Risk Type | Challenge Description | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Logistical Complexity | Overlapping schedules, resources | Use real-time coordination tools |
| Financial Constraints | Budget conflicts among departments | Set clear spending limits and review |
| Communication Failure | Information silos and misunderstandings | Implement robust communication protocols |
Pro tip: Develop a comprehensive risk management framework that includes predefined escalation procedures and establishes clear accountability metrics for each team member's responsibilities.
Comparing Shared Tools and Traditional Methods
Event planning methodologies have undergone significant transformation, with digital shared tools fundamentally challenging traditional coordination approaches. Traditional event planning models relied heavily on manual processes, physical documentation, and direct personal interactions, which limited scalability and real-time collaboration. Modern shared tools represent a paradigm shift, introducing digital platforms that enable instantaneous communication, centralized resource management, and dynamic workflow adaptations.
The key differences between shared tools and traditional methods manifest across several critical dimensions. Traditional approaches typically involve sequential communication channels, where information passes through hierarchical structures, creating potential bottlenecks and delays. Shared digital platforms, by contrast, enable simultaneous multi-directional communication, allowing team members to interact, update, and respond in real time. This fundamental shift reduces coordination overhead, minimizes miscommunication risks, and accelerates decision-making processes across geographically distributed teams.
Advanced shared tools offer sophisticated features that traditional methods cannot replicate, including automated scheduling, predictive analytics, integrated communication channels, and comprehensive data tracking. These technologies provide granular insights into team performance, resource allocation, and potential scheduling conflicts. Organizations can now leverage machine learning algorithms and collaborative interfaces to optimize event planning strategies, something impossible within traditional linear planning frameworks that depended primarily on manual interventions and personal relationships.
Here's a quick reference comparing shared event planning models and traditional event planning methods:
| Aspect | Shared Event Planning | Traditional Event Planning |
|---|---|---|
| Collaboration Level | Cross-functional teamwork | Single coordinator control |
| Decision-Making | Distributed and adaptive | Centralized and hierarchical |
| Technology Usage | Digital collaboration tools | Paper-based/manual systems |
| Scalability | Easily scalable | Limited by manual processes |
Pro tip: Implement a phased transition strategy when adopting shared event planning tools, ensuring gradual technology integration and providing comprehensive training to minimize resistance and maximize team adoption.
Simplify Shared Event Planning with WhenNOT Today
The article highlights how shared event planning requires clear communication, flexible collaboration, and real-time coordination across diverse teams. If you often struggle with managing complex schedules and aligning multiple stakeholders, the pain of overlapping dates and endless back-and-forth is familiar. WhenNOT understands these challenges and offers a solution that transforms shared planning into a seamless experience. By focusing on an "inverse scheduling" approach, WhenNOT helps you avoid traditional confusion by asking participants when they are unavailable instead of when they are available. This strategy is perfect for teams facing logistical complexity and communication failures, as stressed in the article.
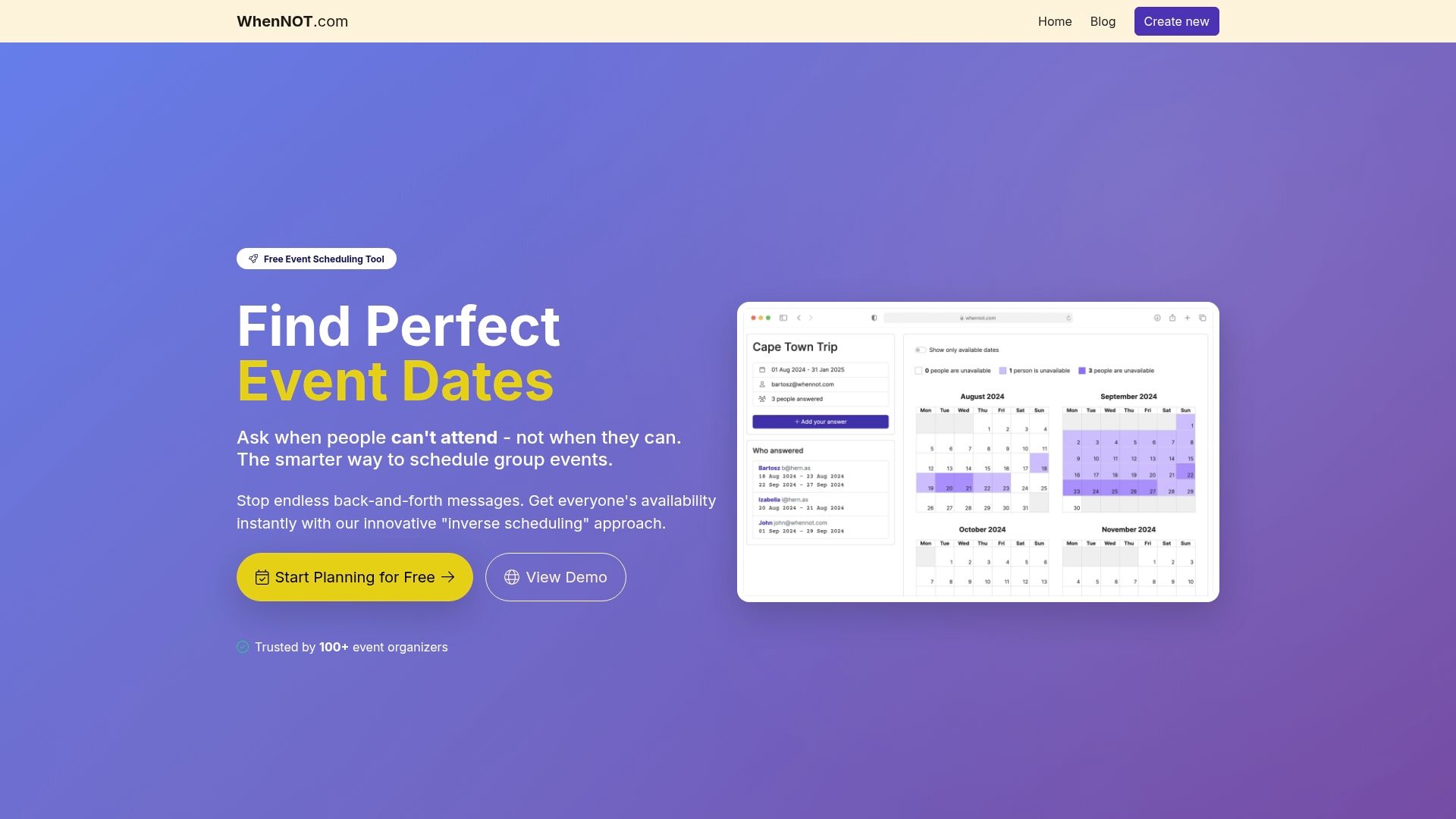
Start streamlining your collaborative event planning now with WhenNOT. Easily create events, share unique links, and visualize busy days all in one user-friendly platform. Experience faster decisions, fewer communication delays, and enhanced transparency for your multi-day or flexible date events. Visit WhenNOT to get started today and turn shared event planning challenges into organized, stress-free success. Learn more about effective collaborative participation strategies by exploring this resource and discover how our digital approach complements the future of event coordination.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is shared event planning?
Shared event planning is a collaborative approach to organizing events, where multiple stakeholders work together, distributing responsibilities and integrating diverse expertise to enhance the overall planning process.
What are the benefits of shared event planning models?
The benefits include enhanced collaboration, reduced individual workload, effective use of resources, and the ability to leverage specialized skills from different departments to ensure comprehensive event coverage.
How does shared event planning differ from traditional event management?
Shared event planning emphasizes cross-functional teamwork and distributed decision-making, whereas traditional management typically involves a single coordinator who handles all details in a centralized manner.
What tools are essential for effective shared event planning?
Essential tools include digital collaboration platforms that support task management, real-time communication, and visibility into team contributions, making it easier to coordinate complex events across distributed teams.
Recommended
- Understanding Community Event Planning Guide for Everyone - WhenNOT Blog
- Complete Guide to Event Planning for Communities - WhenNOT Blog
- Event Organization Strategies: Complete Guide - WhenNOT Blog
- 7 Habits of Successful Event Organizers You Should Adopt - WhenNOT Blog
- Intranet content ideas
- Wat is een netwerkevenement: zakelijke waarde uitgelegd - Ondernemers Plaza Online
