Relying on traditional sign-up scheduling can leave even experienced event coordinators facing headaches, especially when planning flexible multi-day events. Across American and European companies, more than 30% of scheduled slots go unused due to outdated registration processes. Simplifying the way teams and participants confirm their availability leads to smoother coordination and more productive outcomes. Discover practical insights that help eliminate manual sign-ups so every event runs with less friction and greater efficiency.
Table of Contents
- Sign-Up Scheduling Defined And Common Issues
- Traditional Sign-Up Models Versus No-Sign-Up Methods
- Privacy, Accessibility, And User Experience Impact
- Efficiency Gains And Reduced Delays In Group Scheduling
- Risks, Limitations, And Best Use Cases Compared
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Flexibility in Scheduling | Adopting flexible scheduling methods enhances participant engagement by minimizing rigid commitments. |
| Enhanced User Experience | Prioritizing minimal personal information and intuitive interfaces fosters greater accessibility and encourages participation. |
| Operational Efficiency | Automated scheduling significantly reduces administrative overhead and scheduling conflicts, promoting smoother event management. |
| Contextual Relevance | Matching the scheduling method to specific event requirements is crucial for optimizing outcomes and participant satisfaction. |
Sign-Up Scheduling Defined and Common Issues
Sign-up scheduling represents a traditional event planning approach where participants manually register for specific time slots or resources through a predefined registration system. At its core, this method involves individuals selecting and confirming their availability by actively submitting their preferences through a sign-up platform or interface. While seemingly straightforward, scheduling challenges can significantly impact resource allocation and event efficiency.
Traditional sign-up scheduling models typically suffer from multiple inherent limitations that compromise their effectiveness. These challenges include inflexible time slot allocation, high potential for scheduling conflicts, and limited adaptability to changing participant needs. Research indicates that such systems often struggle with critical operational issues like managing peak workload times and addressing dynamic user preferences. Specifically, under-utilization emerges as a significant problem, with many scheduled slots remaining unused due to no-shows or inefficient reservation mechanisms.
The fundamental weaknesses of sign-up scheduling stem from its rigid structural design. Most traditional systems require participants to actively commit to specific times, which creates unnecessary complexity and friction in the scheduling process. This approach demands substantial manual coordination, increases administrative overhead, and frequently results in suboptimal time allocation. By forcing participants into a constrictive framework, sign-up scheduling inadvertently creates barriers that make event planning more challenging rather than more streamlined.
Pro Tip: Consider adopting flexible scheduling alternatives that allow participants to indicate unavailable times instead of requiring strict commitment to specific slots.
Traditional Sign-Up Models Versus No-Sign-Up Methods
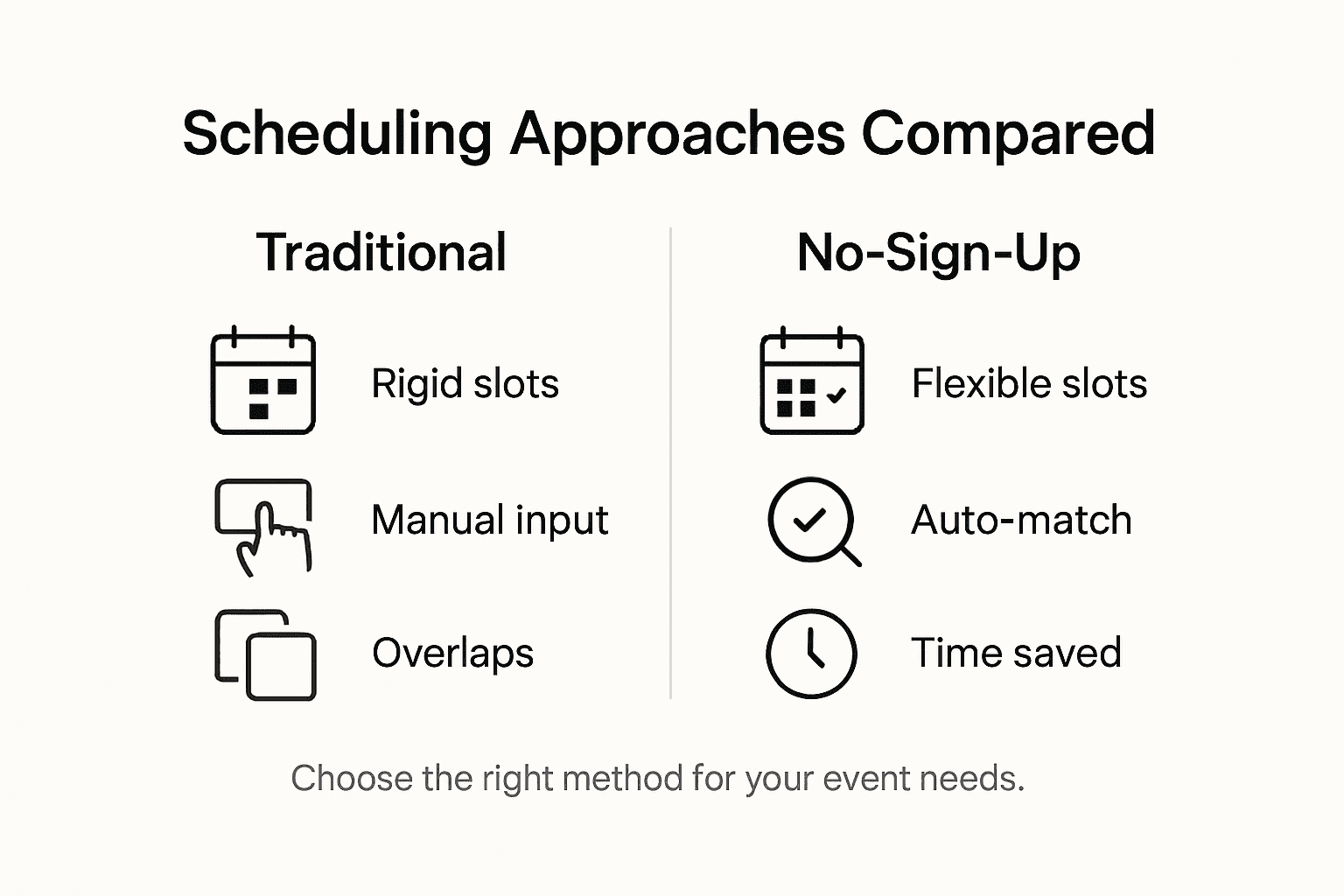
Traditional sign-up models and no-sign-up methods represent fundamentally different approaches to scheduling and resource allocation. While traditional methods require participants to actively select and commit to specific time slots, no-sign-up frameworks optimize resource use through dynamic, automated scheduling mechanisms. These alternative approaches eliminate the manual registration process, instead focusing on creating more fluid and efficient scheduling experiences.
The key distinctions between these models become apparent when examining their operational characteristics. Traditional sign-up systems typically involve manual participant selection, creating numerous potential friction points. Participants must navigate complex registration interfaces, select specific time slots, and commit to rigid schedules. In contrast, no-sign-up methods leverage intelligent algorithms that automatically match availability and preferences without requiring explicit user registration. Automated scheduling reduces administrative overhead, minimizes scheduling conflicts, and provides a more seamless experience for all participants.
Comparative analysis reveals significant advantages of no-sign-up approaches. These systems can dynamically adjust appointments, reduce resource underutilization, and create more flexible scheduling environments. By removing the barrier of manual sign-ups, organizations can streamline their event planning processes, reduce administrative workload, and create more adaptable scheduling frameworks. The shift from manual to automated scheduling represents a fundamental transformation in how resources and time are managed across various professional and personal contexts.
Here is a summary of key differences between traditional sign-up models and no-sign-up methods:
| Aspect | Traditional Sign-Up Model | No-Sign-Up Method |
|---|---|---|
| Registration Process | Manual selection of time slots | Algorithm-driven assignment |
| User Involvement | High, requires active input | Low, passive participation |
| Flexibility | Rigid and structured | Adaptive and dynamic |
| Administrative Effort | Intensive manual management | Minimal human intervention |
Pro Tip: Consider implementing scheduling solutions that prioritize participant flexibility and minimize manual registration steps.
Privacy, Accessibility, and User Experience Impact
Scheduling systems fundamentally shape user interactions, with privacy and accessibility emerging as critical considerations in modern event planning. User experience is dramatically influenced by the complexity of registration processes, which can introduce significant barriers to participation. Traditional sign-up models often create unnecessary friction by demanding extensive personal information, complex registration steps, and rigid commitment requirements that can alienate potential participants.
Accessibility goes beyond mere technical functionality. Privacy protection becomes paramount when evaluating scheduling approaches, with no-sign-up methods offering a more user-centric alternative. These innovative systems minimize personal data collection, reduce cognitive load during scheduling, and provide more inclusive interfaces that accommodate diverse user needs. By eliminating mandatory account creation and extensive form-filling, organizations can create more welcoming and approachable scheduling environments that respect individual preferences and technological comfort levels.
The impact of user experience extends far beyond simple convenience. Poorly designed scheduling systems can create psychological barriers that discourage participation, particularly among users who are less technologically confident or who value their personal information privacy. Advanced scheduling approaches that prioritize minimal data collection, intuitive interfaces, and flexible participation models demonstrate a profound understanding of user autonomy. These methods recognize that the most effective scheduling solutions are those that feel seamless, transparent, and respectful of individual user constraints and preferences.

Pro Tip: Select scheduling tools that require minimal personal information and offer clear, straightforward participation options.
Efficiency Gains and Reduced Delays in Group Scheduling
Group scheduling represents a complex challenge that demands innovative solutions to minimize operational friction and maximize time efficiency. Automated scheduling approaches can dramatically reduce service delays by distributing appointment allocation more strategically, effectively transforming how organizations manage collective time management. Traditional sign-up methods create bottlenecks by requiring manual coordination, whereas modern scheduling techniques leverage intelligent algorithms to streamline the entire process.
The operational overhead associated with manual scheduling creates significant hidden costs for organizations. Conventional methods require extensive back-and-forth communication, multiple touch points for coordination, and substantial administrative effort to reconcile individual availability. No-sign-up scheduling solutions eliminate these inefficiencies by automatically detecting optimal time windows, reducing the cognitive load on participants, and creating more transparent scheduling environments that adapt dynamically to group constraints.
Advanced scheduling methodologies fundamentally reframe time allocation as a collaborative, intelligent process rather than a bureaucratic exercise. By minimizing idle times and eliminating unnecessary waiting periods, these approaches can transform group scheduling from a potential source of frustration into a seamless, almost invisible process. The key lies in understanding that efficiency is not just about saving minutes, but about creating more meaningful, productive interactions that respect each participant's time and energy.
Pro Tip: Prioritize scheduling tools that offer real-time availability matching and require minimal manual intervention.
Risks, Limitations, and Best Use Cases Compared
No-sign-up scheduling approaches represent a significant evolution in event coordination, but they are not without nuanced challenges. Unlike traditional sign-up methods, these innovative systems introduce a complex landscape of potential risks and strategic advantages. Understanding the precise boundaries of their effectiveness becomes crucial for organizations seeking to optimize their scheduling processes and minimize potential operational disruptions.
The technological constraints of no-sign-up scheduling systems emerge from their heavy reliance on algorithmic precision. While these methods dramatically reduce manual coordination efforts, they simultaneously introduce potential limitations in user autonomy and customization. Complex backend management requirements mean that these systems work exceptionally well for large-scale, predictable events with standardized participation patterns, but may struggle with highly individualized scheduling scenarios that demand granular user input and frequent dynamic adjustments.
Contextual application remains the critical determinant of scheduling approach success. Traditional sign-up models retain advantages in smaller, more nuanced group settings where individual preferences and specific constraints require detailed negotiation. Conversely, no-sign-up methods excel in environments with high participant volumes, repeatable scheduling patterns, and minimal variability. The key lies in carefully matching the scheduling approach to the specific organizational context, recognizing that no single method provides a universal solution across all potential scenarios.
Below is a reference table outlining the best use cases for each scheduling approach:
| Scheduling Method | Ideal Use Case | Primary Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Sign-Up | Small groups with unique needs | High manual coordination |
| No-Sign-Up (Automated) | Large events with standard schedules | Less user customization |
Pro Tip: Conduct a thorough assessment of your event's specific requirements before selecting a scheduling approach, prioritizing flexibility and participant experience.
Discover a Smarter Alternative to Traditional Sign-Up Scheduling
The challenges highlighted in the article around traditional sign-up scheduling—such as rigid time slot commitment, high administrative overhead, and privacy concerns—are exactly what WhenNOT was created to solve. By asking participants only when they are unavailable rather than requiring them to sign up for specific times, WhenNOT removes the friction of manual registration and reduces scheduling conflicts. This innovative approach respects privacy, requires no account creation, and offers a flexible solution especially effective for multi-day or flexible date events.
Transform your event planning experience today by trying this free, user-friendly tool that streamlines group scheduling while protecting participant autonomy. Take advantage of WhenNOT’s visual availability summaries and minimal administrative effort to save time and reduce delays. Don’t let outdated, inefficient scheduling hold your events back. Visit WhenNOT’s landing page now and start coordinating effortlessly with your group in minutes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why should I avoid traditional sign-up scheduling for event planning?
Traditional sign-up scheduling is often inflexible and prone to conflicts, which can lead to under-utilization of slots, increased administrative overhead, and a more challenging planning process.
How do no-sign-up scheduling methods improve efficiency?
No-sign-up methods use automated scheduling, which reduces the need for manual registration and coordination, eliminating bottlenecks and streamlining the scheduling process, thus enhancing efficiency.
What are the key differences between traditional sign-up models and no-sign-up methods?
Traditional sign-up models require manual selection of time slots and involve high user involvement, while no-sign-up methods use algorithms for automatic scheduling with low user input, offering more flexibility and reducing administrative effort.
How do scheduling systems impact user experience?
Scheduling systems that demand extensive personal information and complex registrations create friction and can deter participation. No-sign-up methods tend to provide a smoother, more user-centric experience by minimizing data collection and simplifying participation.
Recommended
- Top Scheduling Mistakes to Avoid for Stress-Free Planning - WhenNOT Blog
- Role of Sign-Up Free Tools: Complete Guide to Benefits - WhenNOT Blog
- 7 Group Planning Time Savers for Faster Event Coordination - WhenNOT Blog
- 6 Ways to Simplify Scheduling for Events Easily - WhenNOT Blog
- Event Signage Checklist 2025: Essential Guide for London Businesses - PromoSigns.co.uk
- Scheduling Production Planning and Control for Film Shoots
