Nearly 40 percent of American teams say scheduling group meetings is their biggest time management headache. With remote work on the rise and more organizations collaborating across time zones, finding a meeting that fits everyone’s calendar can feel impossible. Adopting collaborative scheduling is helping modern groups overcome the chaos and eliminate much of the back-and-forth that once slowed American workplace productivity, while also dispelling long-held myths about group coordination.
Table of Contents
- Defining Collaborative Scheduling And Common Myths
- Types Of Collaborative Scheduling Models
- How Collaborative Scheduling Platforms Operate
- Benefits And Challenges For Group Organizers
- Comparing Collaborative And Traditional Scheduling Methods
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Collaborative Scheduling Transforms Coordination | This method shifts scheduling from a top-down approach to a collective negotiation, enhancing participant engagement and minimizing administrative burdens. |
| Models of Collaborative Scheduling | Three effective models—consensus-based, democratic, and algorithmic—cater to varying group sizes and complexity, optimizing overall scheduling efficiency. |
| Platforms Enhance Scheduling Processes | Advanced collaborative scheduling platforms simplify event coordination through user-friendly interfaces and algorithmic support, promoting real-time collaboration among participants. |
| Benefits Outweigh Challenges for Organizers | While collaborative scheduling improves communication and reduces conflicts, organizers must address technological literacy and privacy concerns to ensure successful implementation. |
Defining Collaborative Scheduling and Common Myths
Collaborative scheduling represents a strategic approach to coordinating group events by leveraging collective input and synchronizing availability across multiple participants. At its core, this method transforms traditional scheduling from a linear, top-down process into a dynamic, collaborative experience. Computer-supported cooperative work models demonstrate how technology enables teams to coordinate more effectively across different contexts and time zones.
Unlike conventional scheduling techniques that rely on single administrators dictating meeting times, collaborative scheduling empowers all participants to contribute their constraints and preferences. This approach recognizes that scheduling is fundamentally a group negotiation, not just an administrative task. The key principles involve transparency, mutual accommodation, and efficient communication. Participants share their unavailable periods, creating a comprehensive view of collective availability rather than forcing individuals to conform to predefined time slots.
Common myths surrounding collaborative scheduling often stem from misunderstandings about its complexity and effectiveness. Many people mistakenly believe that group scheduling must be complicated or time-consuming. In reality, modern collaborative scheduling tools streamline the process by simplifying input methods and rapidly identifying optimal meeting windows. Synchronous and asynchronous collaboration research reveals that strategic approaches can significantly reduce coordination overhead.
Key misconceptions include the belief that everyone must be available simultaneously, that scheduling requires extensive back-and-forth communication, or that group coordination inherently creates conflicts. Collaborative scheduling actually minimizes these challenges by providing structured, user-friendly mechanisms for sharing availability. By focusing on collective needs and leveraging intuitive tools, groups can transform scheduling from a potential source of frustration into a smooth, inclusive process that respects everyone's time and constraints.
Types of Collaborative Scheduling Models
Collaborative scheduling encompasses several strategic models designed to address diverse group coordination challenges. These models range from simple shared calendar approaches to sophisticated algorithmic systems that optimize complex scheduling scenarios. Multi-objective collaborative scheduling algorithms demonstrate how advanced computational techniques can dramatically improve scheduling efficiency across various contexts.
Three primary collaborative scheduling models emerge as particularly effective: consensus-based, democratic, and algorithmic scheduling. Consensus-based scheduling involves group members actively negotiating and agreeing on meeting times through direct communication and mutual compromise. This approach prioritizes collective agreement and ensures everyone feels heard. Democratic scheduling introduces voting mechanisms where participants rank or select preferred time slots, with the most popular options becoming the final schedule. This method works particularly well for larger groups with diverse availability.
The algorithmic scheduling model represents the most technologically advanced approach. Collaborative scheduling research in supply chain systems reveals how intelligent algorithms can analyze complex availability constraints and generate optimal scheduling solutions. These models utilize machine learning and computational techniques to rapidly identify time windows that minimize conflicts and maximize participant convenience. Advanced systems can consider multiple variables simultaneously, such as individual preferences, geographic time zones, and recurring scheduling patterns.
Each collaborative scheduling model offers unique advantages depending on group size, complexity, and specific coordination requirements. Small teams might benefit from consensus-based approaches that encourage direct dialogue, while larger organizations may require more sophisticated algorithmic solutions. The key is selecting a model that balances technological efficiency with human flexibility, recognizing that scheduling is ultimately about connecting people and respecting their individual constraints.
How Collaborative Scheduling Platforms Operate
Collaborative scheduling platforms function through sophisticated technological infrastructure that transforms traditional event coordination processes. These platforms leverage advanced algorithms and user-friendly interfaces to simplify complex scheduling challenges. Collaborative scheduling software frameworks provide essential computational building blocks that enable seamless interaction and intelligent scheduling optimization across diverse group contexts.
The core operational mechanism of these platforms typically involves several key stages. First, participants receive a unique invitation link where they can input their availability and scheduling constraints. Availability mapping becomes the foundational step, where the platform aggregates individual schedules to identify potential common time windows. Intelligent systems analyze these inputs using advanced computational techniques, comparing preferences, blocking out unavailable periods, and dynamically suggesting optimal meeting times that minimize conflicts.

Collaborative construction scheduling technologies reveal that modern platforms incorporate sophisticated features beyond basic time matching. Real-time collaborative editing allows multiple users to simultaneously update and view scheduling information, ensuring transparency and immediate synchronization. Advanced platforms integrate artificial intelligence algorithms that can predict scheduling challenges, assess potential conflicts, and recommend alternative time slots based on historical interaction patterns and participant preferences.
The technical architecture of collaborative scheduling platforms emphasizes user experience, data security, and computational efficiency. By removing traditional barriers like manual coordination and extensive email exchanges, these platforms transform scheduling from a complex negotiation into a streamlined, intuitive process. The ultimate goal remains consistent: creating a flexible, inclusive environment where groups can effortlessly find mutual time windows while respecting individual constraints and preferences.
Benefits and Challenges for Group Organizers
Group event organizers face a complex landscape of opportunities and potential obstacles when implementing collaborative scheduling strategies. Collaborative scheduling approaches in professional environments demonstrate significant potential for improving team coordination, profitability, and overall organizational efficiency. The primary advantages include enhanced communication, reduced scheduling conflicts, and more transparent decision-making processes.
The benefits of collaborative scheduling for group organizers are multifaceted. Time efficiency emerges as the most prominent advantage, allowing organizers to eliminate endless email chains and manual availability tracking. Platforms enable real-time coordination, where participants can instantly update and view scheduling information. Additionally, these tools provide comprehensive visibility into group availability, helping organizers quickly identify optimal meeting windows and reduce the administrative burden associated with traditional scheduling methods.
Research on collaborative learning dynamics reveals that collaborative scheduling also presents unique challenges group organizers must navigate. Potential obstacles include varying participant engagement levels, technological literacy differences, and potential privacy concerns. Successful implementation requires careful communication, clear guidelines, and selecting user-friendly platforms that accommodate diverse technological comfort levels. Organizers must proactively address potential resistance by demonstrating the tangible benefits and ease of use of collaborative scheduling tools.
Ultimately, the most effective group organizers view collaborative scheduling as a strategic approach rather than merely a technological solution. By understanding both the powerful advantages and potential limitations, they can create more inclusive, efficient, and responsive scheduling environments. The key lies in selecting appropriate tools, establishing clear communication protocols, and maintaining flexibility to adapt to the unique dynamics of each group's scheduling needs.
Comparing Collaborative and Traditional Scheduling Methods
Traditional scheduling methods have long been characterized by linear, top-down approaches that prioritize administrative control over participant flexibility. Comparative research on synchronous and asynchronous collaboration techniques reveals significant limitations in conventional scheduling strategies that fail to accommodate modern team dynamics and diverse participant constraints.
Traditional scheduling typically involves a single coordinator who manually collects availability through emails, phone calls, or spreadsheets, creating significant administrative overhead. Centralized decision-making becomes the primary bottleneck, where one person shoulders the entire coordination burden. In contrast, collaborative scheduling democratizes the process, allowing all participants to contribute their preferences simultaneously. This approach transforms scheduling from a unilateral task into a collective negotiation, reducing communication delays and increasing overall group satisfaction.
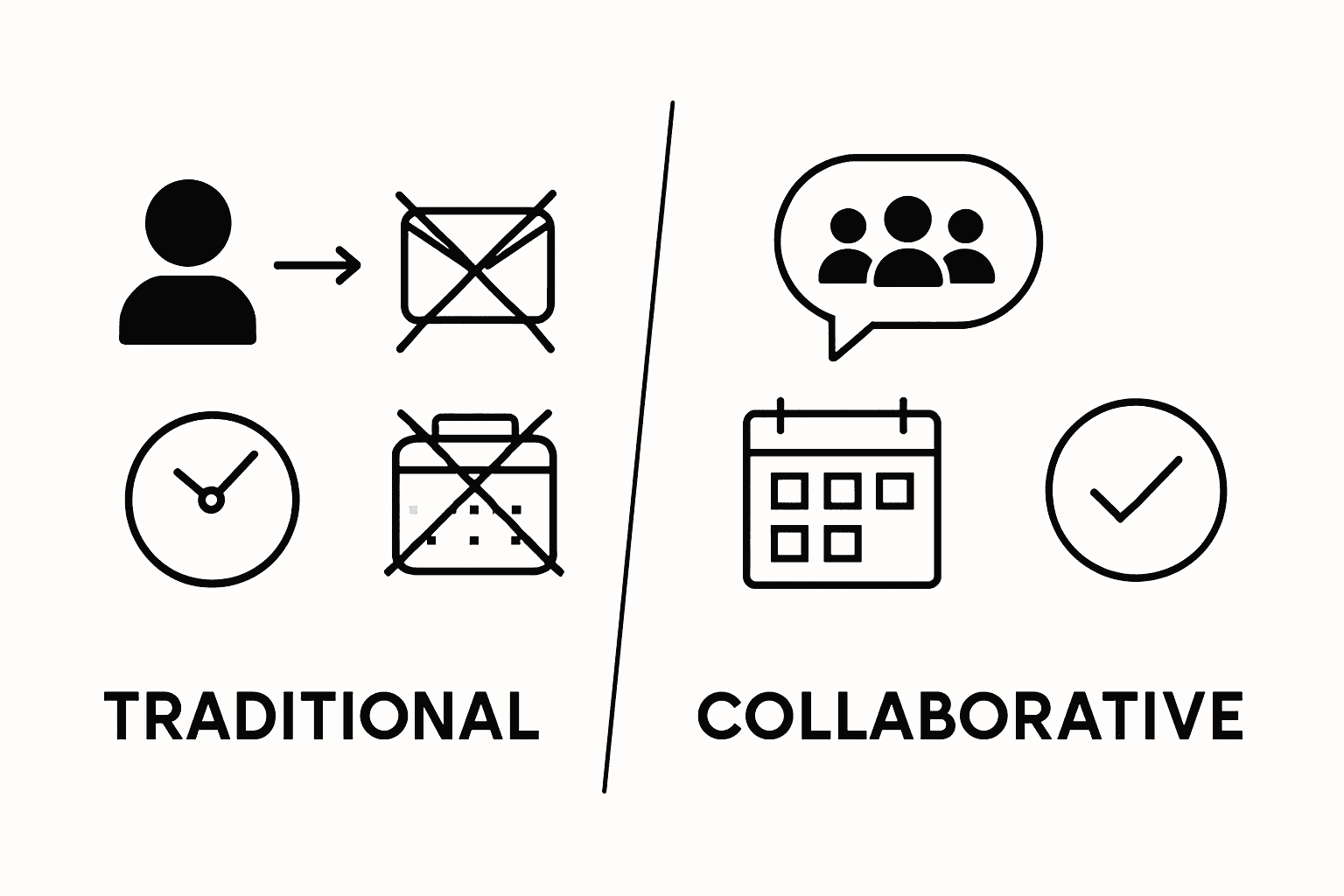
Advanced ensemble collaboration methods demonstrate that modern scheduling approaches can significantly outperform traditional techniques by integrating multiple perspectives and computational strategies. Key differences emerge across several critical dimensions. Traditional methods often rely on rigid time slots and require participants to adapt to preset schedules, while collaborative platforms enable dynamic, flexible scheduling that respects individual constraints. The technological infrastructure of collaborative tools allows for real-time updates, instant conflict resolution, and comprehensive visibility into group availability.
Ultimately, the transition from traditional to collaborative scheduling represents more than a technological upgrade. It reflects a fundamental shift in understanding group coordination as a cooperative process rather than an administrative task. By prioritizing participant flexibility, transparency, and shared decision-making, collaborative scheduling methods create more inclusive, efficient, and responsive planning environments that adapt to the complex realities of modern team interactions.
Simplify Collaborative Scheduling with WhenNOT
Collaborative scheduling offers a promising solution to streamline group event planning by empowering participants to share their availability and constraints. However, as the article highlights, challenges like time-consuming back-and-forth, complex negotiations, and privacy concerns often create frustration for organizers and attendees alike. If you are seeking to transform scheduling from a source of stress into an efficient, inclusive experience, WhenNOT provides a refreshing alternative. Our unique inverse scheduling approach allows participants to mark when they are not busy, making it far easier to identify optimal dates without endless emails or account sign-ups.
Discover how WhenNOT revolutionizes your group coordination by giving you:
- A simple, intuitive platform that visualizes everyone’s busy dates simultaneously
- Privacy-first design with no accounts needed for participants
- Flexibility perfect for multi-day events and complex availability patterns
Start planning your next event with ease and confidence by visiting WhenNOT today. See how thoughtful technology removes the headache from scheduling and makes collaboration a truly seamless process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is collaborative scheduling?
Collaborative scheduling is a method of coordinating group events by allowing all participants to input their availability, fostering a collective approach to finding mutually convenient meeting times.
How do collaborative scheduling platforms work?
Collaborative scheduling platforms operate by allowing participants to share their availability through a unique invitation link. The platform aggregates this information to suggest optimal meeting times while accommodating everyone's constraints.
What are the benefits of using collaborative scheduling?
The benefits of collaborative scheduling include enhanced communication, reduced scheduling conflicts, time efficiency, and improved transparency in the decision-making process for group event planning.
What are the different models of collaborative scheduling?
The primary models of collaborative scheduling include consensus-based scheduling (where members negotiate times), democratic scheduling (where participants vote on preferred times), and algorithmic scheduling (which uses sophisticated algorithms to find optimal meeting windows).
Recommended
- Collaborative Scheduling Workflow: Complete Guide - WhenNOT Blog
- Understanding Why Choose Group Scheduling for Events - WhenNOT Blog
- Master Team Scheduling Best Practices for Success - WhenNOT Blog
- Understanding the Group Scheduling Process for Events - WhenNOT Blog
- The Essential Guide to Importance of Family Meetings - Mastering Conflict
- AI Pickup Scheduling Calls
