Did you know that 75 percent of group projects fail because of poor scheduling and coordination? Trying to align busy calendars can turn even the simplest plans into a headache. With so many moving parts, finding one time that works for a whole team feels nearly impossible. Discover how new collaborative scheduling strategies can take the stress out of group planning and make seamless coordination a reality for everyone.
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Collaborative Scheduling | A collaborative scheduling workflow enhances task coordination by allowing participants to transparently share constraints and availability. |
| Types of Methods | Various collaborative scheduling methods, such as multi-agent planning and gang scheduling, address specific group coordination challenges effectively. |
| Inverse Scheduling | This innovative approach prioritizes marking unavailability, resulting in faster coordination and less communication overhead. |
| Common Pitfalls | Teams must be aware of potential pitfalls, including unrealistic time estimates and communication breakdowns, to ensure effective scheduling. |
Table of Contents
- Defining Collaborative Scheduling Workflow
- Types of Collaborative Scheduling Methods
- How Inverse Scheduling Simplifies Planning
- Ideal Use Cases For Group Coordination
- Common Pitfalls And How To Avoid Them
Defining Collaborative Scheduling Workflow
A collaborative scheduling workflow is a strategic approach to coordinating tasks, events, and resources across multiple individuals or groups, enabling seamless coordination and efficient planning. Unlike traditional scheduling methods that rely on individual calendars, this workflow transforms how teams and groups synchronize their availability and commitments.
At its core, collaborative scheduling involves creating a shared planning environment where participants can transparently communicate their constraints, preferences, and availability. Read more about team scheduling best practices to understand how modern tools facilitate this process. According to research in mobile-edge computing systems, collaborative scheduling algorithms aim to optimize three critical parameters:
- Quality of service: Ensuring tasks are allocated efficiently
- Cost management: Minimizing resource expenditure
- Latency reduction: Decreasing time spent on coordination
The workflow typically involves several key stages: initial availability mapping, constraint identification, potential time slot discovery, and final consensus building. Participants contribute their schedules by indicating when they are unavailable, allowing the group to quickly identify optimal meeting or event windows. This inverse scheduling approach dramatically simplifies group coordination, especially for multi-day events or flexible scheduling scenarios like team retreats, family gatherings, or community event planning.
Types of Collaborative Scheduling Methods
Collaborative scheduling methods vary widely, each designed to address unique coordination challenges across different contexts. Learn more about efficient scheduling techniques to enhance your planning strategy. According to research in multi-agent systems, these methods can be categorized into several distinct approaches that facilitate seamless group coordination.
Multi-Agent Planning represents one sophisticated collaborative scheduling technique. As explored in multi-agent planning research, this method involves multiple autonomous agents working together to allocate resources and synchronize activities toward a shared objective. Key characteristics include:
- Dynamic plan merging
- Negotiation between agents
- Distributed decision-making processes
- Adaptive problem-solving strategies
Gang Scheduling offers another innovative approach, particularly relevant in high-performance computing environments. According to research, this method synchronizes related concurrent processes to run simultaneously, maximizing system efficiency and resource utilization. This technique is especially powerful in scenarios requiring precise timing and coordinated computational workflows.
Other collaborative scheduling methods include consensus-based scheduling, where group members collectively determine optimal time slots, and iterative constraint negotiation, which allows participants to progressively refine their availability. These approaches share a common goal: transforming complex group scheduling from a challenging task into a streamlined, cooperative process that respects individual constraints while achieving collective objectives.
Here's a comparison of major collaborative scheduling methods:
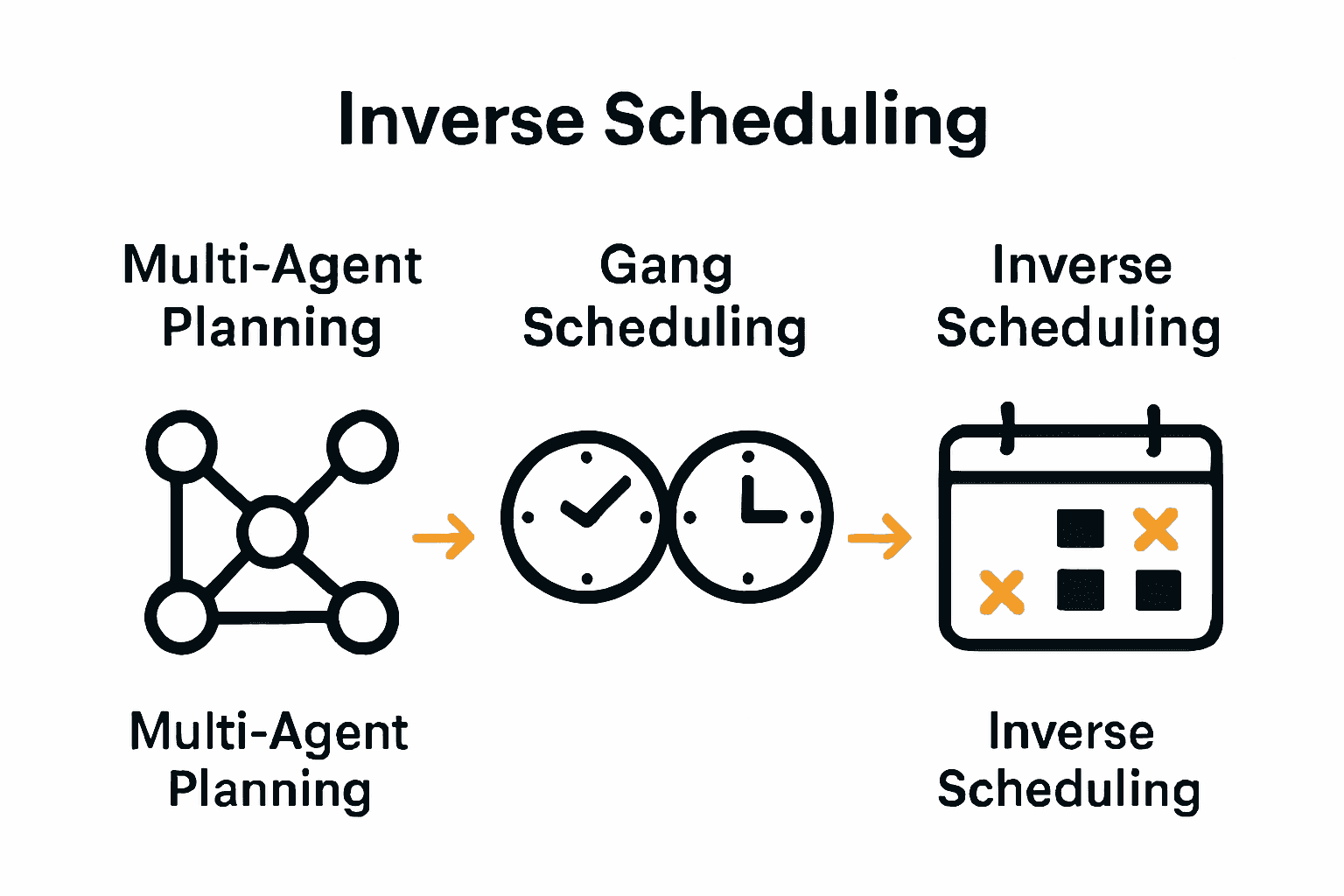
| Method | Key Features | Ideal Contexts |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-Agent Planning | Dynamic plan merging Negotiation Distributed decisions | Complex projects Tech teams |
| Gang Scheduling | Synchronized execution Max system efficiency | High-performance computing |
| Consensus-Based | Collective choice All-member input | Corporate meetings Large groups |
| Iterative Constraint Negotiation | Progressive refinement Conflict resolution | Flexible, multi-party events |
| Inverse Scheduling | Participants mark unavailability Faster consensus | Team retreats Family gatherings |
How Inverse Scheduling Simplifies Planning
Inverse scheduling represents a revolutionary approach to group planning that fundamentally transforms how we coordinate complex events and activities. Learn more about automated scheduling techniques to understand this innovative method. Unlike traditional scheduling where participants share available times, inverse scheduling flips the script by asking people to indicate when they are not available.
According to research on scheduling workflow agents, this method breaks down complex coordination tasks into more manageable microtasks. The core principle is simple yet powerful: instead of everyone listing their free slots (which can be time-consuming and frustrating), participants quickly mark their unavailable times. This approach offers several significant advantages:
- Faster coordination process
- Reduced communication overhead
- More transparent availability mapping
- Minimal cognitive load for participants
The workflow becomes dramatically simplified. Imagine planning a multi-day team retreat or a family gathering where everyone has different schedules. With inverse scheduling, participants can rapidly input their conflicts—work commitments, personal appointments, travel times—creating a collective view of unavailable periods. The remaining open slots become instant candidates for scheduling, eliminating the endless back-and-forth email chains and calendar comparisons that typically plague group planning.

Moreover, this method respects individual privacy and reduces scheduling friction. By focusing on constraints rather than availability, inverse scheduling transforms a potentially stressful negotiation into a straightforward, collaborative process. It's particularly powerful for events with flexible timing, where finding a perfect mutual slot can seem like solving an intricate puzzle.
Ideal Use Cases for Group Coordination
Group coordination techniques are crucial in scenarios requiring complex multi-party planning and synchronized activities. Learn more about group scheduling strategies to explore their wide-ranging applications. From professional environments to personal planning, these methods solve intricate scheduling challenges across diverse contexts.
In professional settings, collaborative scheduling becomes indispensable. According to research on cooperative scheduling algorithms, distributed computing environments particularly benefit from advanced coordination techniques. Key professional use cases include:
- Corporate team retreats and offsite meetings
- Cross-departmental project planning
- Remote team synchronization
- Multinational conference scheduling
- Executive leadership coordination
Personal and social scenarios also demand sophisticated group coordination. Large family gatherings, multi-household vacation planning, and community event organization require nuanced scheduling approaches that accommodate diverse individual constraints. These situations often involve complex logistics like travel times, work schedules, and personal commitments.
Technical and specialized domains present unique collaborative scheduling challenges. Research highlights IoT and edge computing systems as prime examples where distributed task allocation and synchronized scheduling are critical. Scientific research teams, engineering project groups, and technological innovation clusters rely on precise coordination methods to manage complex, interconnected workflows. By leveraging advanced scheduling techniques, these groups can optimize resource allocation, minimize communication overhead, and achieve more efficient collective outcomes.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Collaborative scheduling can quickly become complicated, with numerous potential roadblocks that can derail even the most well-intentioned planning efforts. Learn more about scheduling challenges to develop proactive strategies. Professional research highlights several critical pitfalls that teams and groups must navigate carefully.
According to project management studies, unrealistic time estimates represent one of the most significant scheduling challenges. Key pitfalls include:
- Underestimating task complexity
- Failing to account for individual work styles
- Overlooking potential contingencies
- Neglecting buffer times for unexpected issues
- Ignoring individual participant constraints
Research from project coordination experts reveals that communication breakdowns frequently undermine collaborative scheduling efforts. Scope creep, missed deadlines, and imbalanced workloads often emerge when team members lack clear role definitions and communication protocols. This can lead to redundant work, disengagement, and ultimately, project failure.
To mitigate these risks, successful groups implement proactive strategies. This includes establishing clear milestones, defining explicit roles, maintaining transparent communication channels, and building flexibility into scheduling frameworks. By anticipating potential challenges and creating robust contingency plans, teams can transform potential scheduling obstacles into opportunities for more effective collaboration and streamlined planning.
Take the Stress Out of Group Scheduling—Try WhenNOT Today
Are you tired of back-and-forth emails and endless calendar comparisons when planning your next team event or family gathering? The article explained how collaborative scheduling often gets complicated by unclear availability, conflicting constraints, and communication delays. With traditional tools, finding a suitable date can feel overwhelming, especially for multi-day events.
WhenNOT solves these challenges by using an inverse scheduling approach. Instead of asking everyone when they are free, participants simply mark only the days they are unavailable. Our tool instantly highlights the best dates for your group, making coordination faster, more private, and incredibly easy. Discover why so many organizers choose the WhenNOT online scheduling tool for effortless event planning. Start your next group event with simplicity and confidence—visit https://whennot.com and see how quickly you can find the perfect date.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a collaborative scheduling workflow?
A collaborative scheduling workflow is a strategic approach that coordinates tasks, events, and resources across multiple individuals or groups, allowing for seamless communication and efficient planning.
How does inverse scheduling work in group planning?
Inverse scheduling allows participants to indicate when they are not available, simplifying the coordination process. Instead of listing free slots, participants mark their conflicts, making it easier to identify optimal meeting times.
What are some common pitfalls in collaborative scheduling?
Common pitfalls include unrealistic time estimates, communication breakdowns, neglecting individual constraints, and failing to account for potential contingencies. To avoid these issues, proactive strategies like clear milestones and transparent communication should be implemented.
Which collaborative scheduling methods are most effective for large groups?
Effective collaborative scheduling methods for large groups include consensus-based scheduling for collective time choices, iterative constraint negotiation for refinements, and multi-agent planning for complex projects that require distributed decision-making.
